Dual-wavelength lasers for THz generation
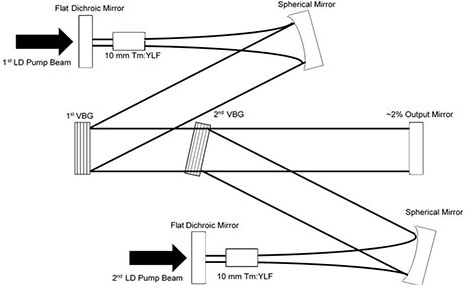
The generation of tunable narrowband terahertz (THz) radiation has shown much interest in recent years. THz systems are used for rotational-vibrational spectroscopy, nondestructive inspection, security screening and others. Monochromatic THz emission has been generated by means of THz parametric oscillation, nonlinear difference frequency generation, and quantum cascade lasers. Intracavity difference frequency generation (DFG) in nonlinear crystals such as gallium arsenide (GaAs) is known as an efficient way to generate a continuous wave THz radiation. A novel high power solid state resonator with the use of volume Bragg grating (VBG) technology to create a dual channel system by spectral beam combination is a topic of this research. The system consists of two separate Tm:YLF crystals and two VBGs for narrowband wavelength selection. At the end of the resonator both channels share common spherical mirrors, which provide feedback and focuses the beam for nonlinear purposes. This allows each channel to be independent in power and wavelength, eliminating gain competition and allowing individual wavelength tunability. The VBGs are recorded in photo-thermo-refractive glass, which has a high laser induced damage threshold and can withstand the high intracavity power present in the resonator. Tunability of the system has shown spectral spacing from 5 to 20 nm, 0.4 – 1.7 THz, and intracavity continuous wave power levels from 80 to 100 W. By placing the GaAs crystal near the waist, THz radiation can be extracted from the cavity.
Holographic phase elements for beam phase transformations
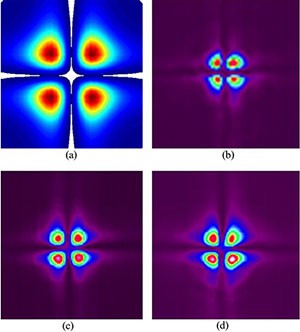
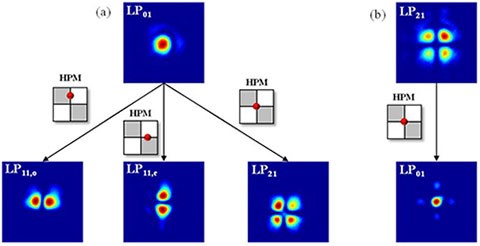
A method to create spectrally tunable phase masks by encoding phase profiles into volume Bragg gratings is investigated. The approach allows these holographic elements to be used as phase masks at any wavelength capable of satisfying the Bragg condition of the hologram. Moreover, it enables the capability to encode and multiplex several phase masks into a single holographic element without cross-talk while maintaining high diffraction efficiency. As examples, we demonstrate fiber mode conversion with near-theoretical conversion efficiency as well as simultaneous mode conversion and beam combining at wavelengths far from the original hologram recording wavelength.
Complex holograms in PTR glass
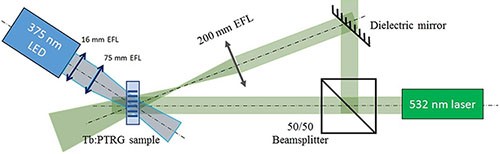
Planar holographic optical elements (volume Bragg gratings, VBGs) recorded in photo-thermo-refractive (PTR) glass are widely used for fine spectral filtering and laser beam control. PTR glass provides photosensitivity in near UV region. Therefore, while planar holographic elements operate in the whole window of transparency – near UV, visible and near IR spectral regions, application of complex (nonplanar) elements is restricted to near UV. A method is investigated to make high-efficiency diffractive optical elements in PTR glass using visible light. The method employs excited state absorption in PTR glass doped with Tb3+. UV radiation was used for excitation to a metastable level of Tb3+ and pulsed radiation at 532 nm was used for hologram recording. Both planar VBGs and holographic lenses operating at 532 nm were demonstrated. Complex holographic optical elements in PTR glass can provide attractive solutions for lasers and spectroscopy replacing conventional optical components.
Multiplexed volume Bragg gratings
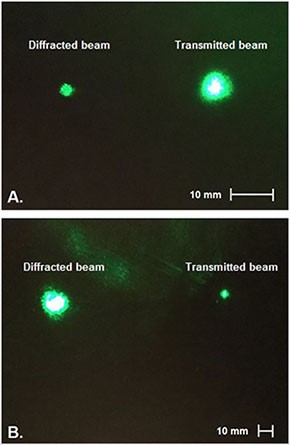
In order to generate high power laser radiation it is often necessary to combine multiple lasers into a single beam. The recent advances in high power spectral beam combining using multiplexed volume Bragg gratings recorded in photo-thermo-refractive glass are presented. The focus is on using multiple gratings recorded within the same volume to lower the complexity of the combining system. Combining of 420 W with 96% efficiency using a monolithic, multiplexed double grating recorded in PTR glass is demonstrated. A multiplexed quadruple grating that maintains high efficiency and good beam quality is demonstrated to pave a way for further scaling of combining channels.
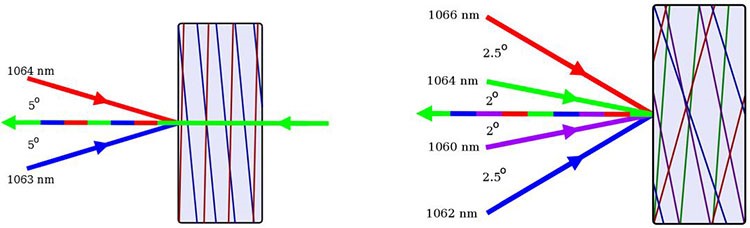
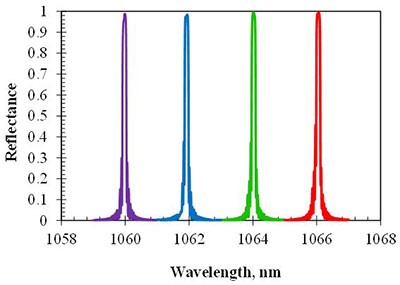
Table 1. Summary of beam combining results at higher power
| Power W | Combining Efficiency | M2,x | M2,y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incident Beam 1 | 135 | – | 1.05 | 1.05 |
| Incident Beam 2 | 150 | – | 1.05 | 1.05 |
| Incident Beam 3 | 143 | – | 1.16 | 1.16 |
| Beam 1 and 2 combined | 282 | 99% | 1.15 | 1.08 |
| All beams combined | 420 | 96% | 1.38 | 1.20 |
Table 2. M2 of beams reflected from a 4x RBG
| Wavelength nm | M2,x | M2,y | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incident Beam | 1060-1066 | 1.13 | 1.20 |
| Reflection from | 1060 | 1.10 | 1.19 |
| Multiplexed | 1062 | 1.12 | 1.19 |
| RBG | 1064 | 1.07 | 1.22 |
| 1066 | 1.10 | 1.23 |